Background
Surgical procedures for gastrointestinal oncology intervention are inevitably highly variable amongst surgeons and centers. Although acceptable to a degree, a substantial proportion of this variability has a potential relevance for both short term clinical outcomes and long term survival. For patients with right-sided colon cancer, a laparoscopic right hemicolectomy (LRHC) is the surgical procedure to remove the cancer and locoregional lymph nodes. This surgical technique has evolved during the last decade with the introduction of the intracorporeal anastomosis, the Pfannenstiel extraction and the complete mesocolic excision (CME). The latter is a dissection technique in embryological planes with a central vascular ligation of the segmental branches at its origin, resulting in an optimal lymphadenectomy. Given the insights from recent studies showing a positive association between the quality of surgery and relevant clinical outcomes, there is a great need to reduce the interinstitutional and intersurgeon variability and to implement an optimized and standardized surgical technique for right-sided colon cancer in the Netherlands to improve short- and long-term clinical and oncological outcomes. This kind of implementation needs a consensus of the key elements of the procedure and a formative quality assessment of LRHC. Detailed objective assessment of the LRHC is currently not performed in clinical practice nor in surgical training. Quality assessment of LRHC has great potential to improve surgical training and furthermore, implementation of a standardized technique will ultimately lead to better quality of care for patients suffering from right-sided colon cancer.
Objective
The main objective of this study is to improve surgical outcomes for patients with right-sided colon cancer by a prospective sequential interventional cohort study that aims to standardize the surgical technique with subsequent controlled implementation after standardized review of the current practice in a nationwide multicenter setting.
Study design
Prospective interventional sequential cohort study with 5 phases.
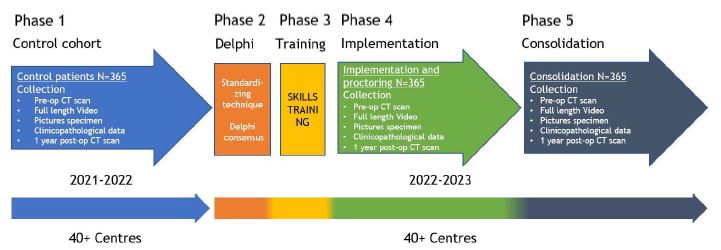
Inclusion criteria
- Planned laparoscopic or robot-assisted (extended) right hemicolectomy for colon cancer (adenocarcinoma) of the caecum, ascending colon, hepatic flexure or proximal transverse colon;
- Age above 18 years;
- Signed informed consent.
Exclusion criteria
- cT4b/multivisceral resection;
- cTNM stage 4 (M1);
- ASA 4;
- Immune modulating medication;
- Prior midline or transverse laparotomy larger than 10 cm (not including Pfannenstiel and McBurney’s incision);
- Perforated disease/peritumoral abscess/fistula;
- Acute obstruction;
- Emergency surgery;
- Neuroendocrine neoplasm (NEN);
- Other primary malignancy treated within 5 years from diagnosis of colon cancer, except for curatively treated prostate, breast, skin and cervical cancer.
Downloads
Algemeen
Ziekenhuizen
Admiraal De Ruyter Ziekenhuis
Albert Schweitzer Ziekenhuis
Alrijne Ziekenhuis
Amstelland Ziekenhuis
Amsterdam UMC, locatie VUmc
Amsterdam UMC, locatie AMC
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
Beatrixziekenhuis Rivas Zorggroep
Canisius Wilhelmina Ziekenhuis
Deventer Ziekenhuis
Diakonessenhuis Utrecht
Elisabeth-TweeSteden Ziekenhuis
Flevoziekenhuis
Franciscus Gasthuis Vlietland
Gelre Ziekenhuizen
Groene Hart Ziekenhuis
Haaglanden Medisch Centrum
IJsselland Ziekenhuis
Ikazia Ziekenhuis
Isala Ziekenhuis
LangeLand Ziekenhuis
Laurentius Ziekenhuis
Leids Universitair Medisch Centrum
Maastricht Universitair Medisch Centrum
Maasziekenhuis Pantein
Meander Medisch Centrum
Medisch Centrum Leeuwarden
Medisch Spectrum Twente
Nij Smellinghe
Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis
Sint Jansgasthuis
Spaarne Gasthuis
Stichting ZorgSaam Zeeuws Vlaanderen
Treant Zorggroep
Van Weel-Bethesda Ziekenhuis
VieCuri Medisch Centrum
Zaans Medisch Centrum
Ziekenhuis Gelderse Vallei
Ziekenhuisgroep Twente
Ziekenhuis St Jansdal
Zuyderland Medisch Centrum
